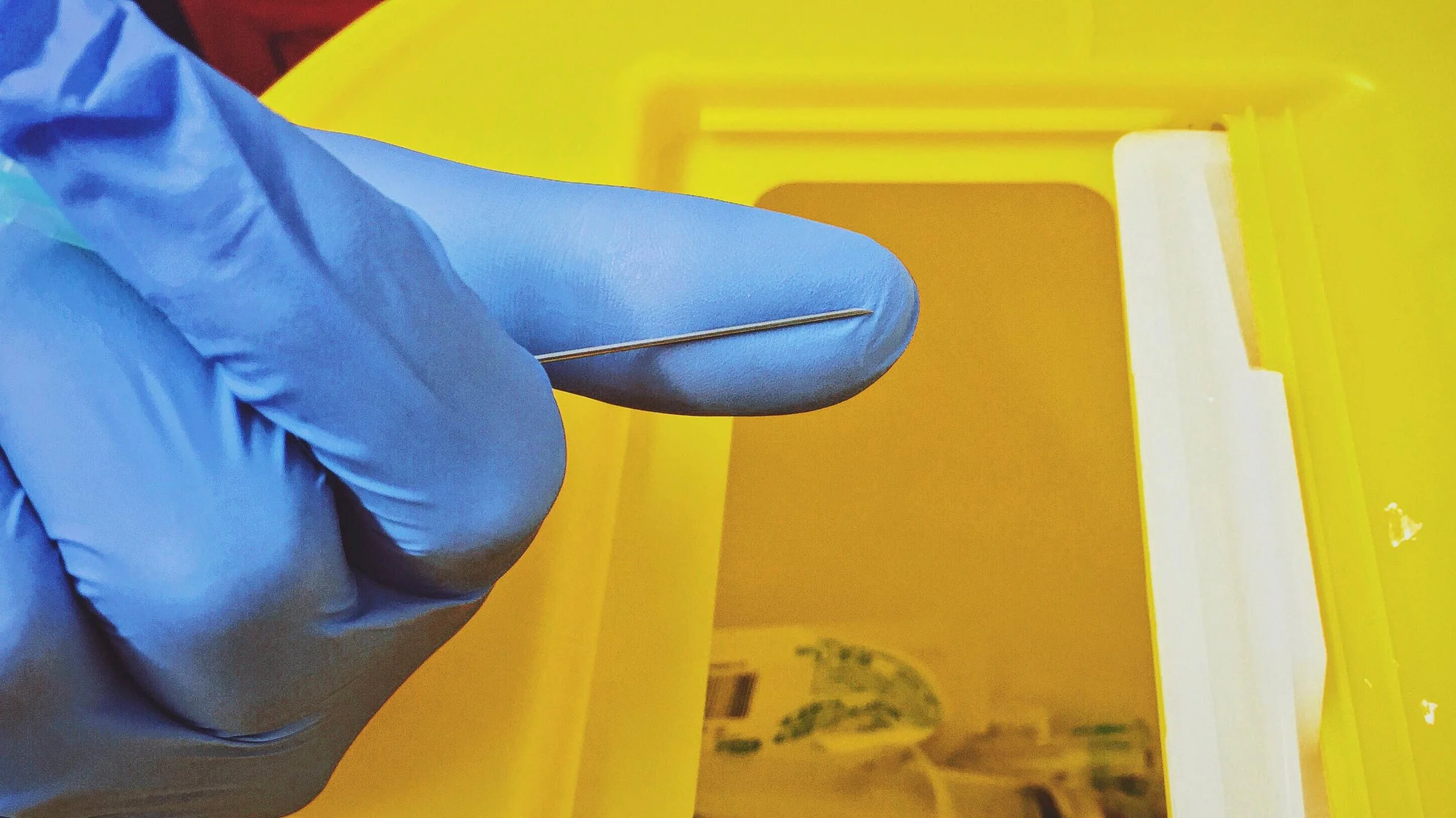
Lightning Learning: Sharps Injuries
““Sharps injuries are the second most common cause of staff injury and account for 17% of all accidents to NHS staff.””
What?
“Breakage of the skin barrier by a potentially contaminated sharp”
Significant exposure: percutaneous – exposure to blood or body fluid from a source known to be HBV surface antigen (HBsAg), HCV, or HIV +ve.
Risk of acquiring BBV after a needlestick (from a positive source)
HBV (1-in-3 or 30%)
HCV (1-in-30 or 3.3%)
HIV (1-in-300 or 0.33%)
Why?
Sharps injuries are the second most common cause of staff injury and account for 17% of all accidents to NHS staff. However, up to 40% of injuries are not reported.
The risk of seroconversion increases with degree of contamination of instrument, depth of puncture, and if needle was in patient’s vein or artery.
Remember to report all sharps injuries!
Further Reading
- eLFH: Sharps Injuries (anaesthetic course)
- RCEM: Needle Stick Injury Position Statement (PDF)