Lightning Learning: AHRF / Type 2 Respiratory Failure
STOP!
Acute hypercapnic respiratory failure (AHRF) or type 2 respiratory failure, is a failure of ventilation leading to acute hypercapnia with an element of hypoxia.
AHRF is seen on an ABG and is defined as:
- PaCO2 > 6kPa
- pH < 7.35
The element of hypoxia can be corrected often with supplemental oxygen to a target SaO2 of 88-92%
Hypercapnia can result in:
- Cardiac arrest
- Respiratory arrest
- Coma
- Seizures
- Arrhythmia
LOOK
AHRF can be life-threatening.
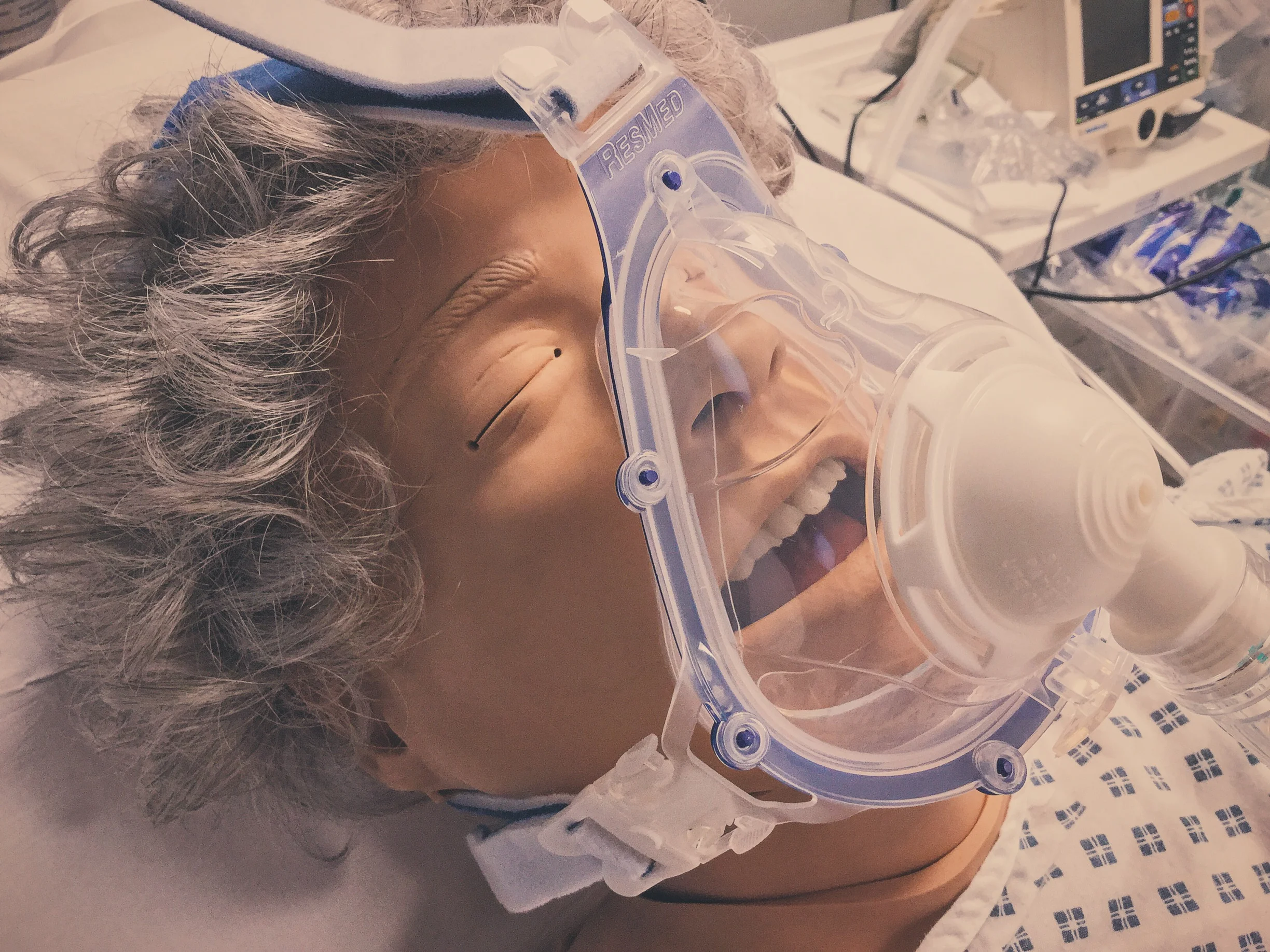
Following maximal medical management, non-invasive ventilation can be used to improve patient's own respiratory effort.
Contraindications to NIV
Absolute:
- Severe facial deformity
- Facial burns
- Fixed upper airway obstruction
- Patient refusal
Relative:
- pH <7.15
- pH <7.25 and additional adverse features
- GCS <8
- Agitation/confusion
- Cognitive impairment
LEARN
Before starting NIV:
- Discuss and document escalation plan and resuscitation status
- Offer lidocaine for ABGs
Further Reading
- BTS/ICS Guidelines for the Ventilatory Management of Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in Adults (BTS)
- Use of acute NIV in patients hospitalised with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infection (BTS)
- Management of acute hypercapnic respiratory failure (UHL)
Many thanks to Dr Darren Whitelaw for creating the original version of this poster 👍