#SimBlog: Tricyclic Antidepressant Overdose
““15 y/o found unresponsive by his father. Has been struggling at school. Left a suicide note and was found next to some empty packets of his mother’s tablets.””
Observations
A – Patent
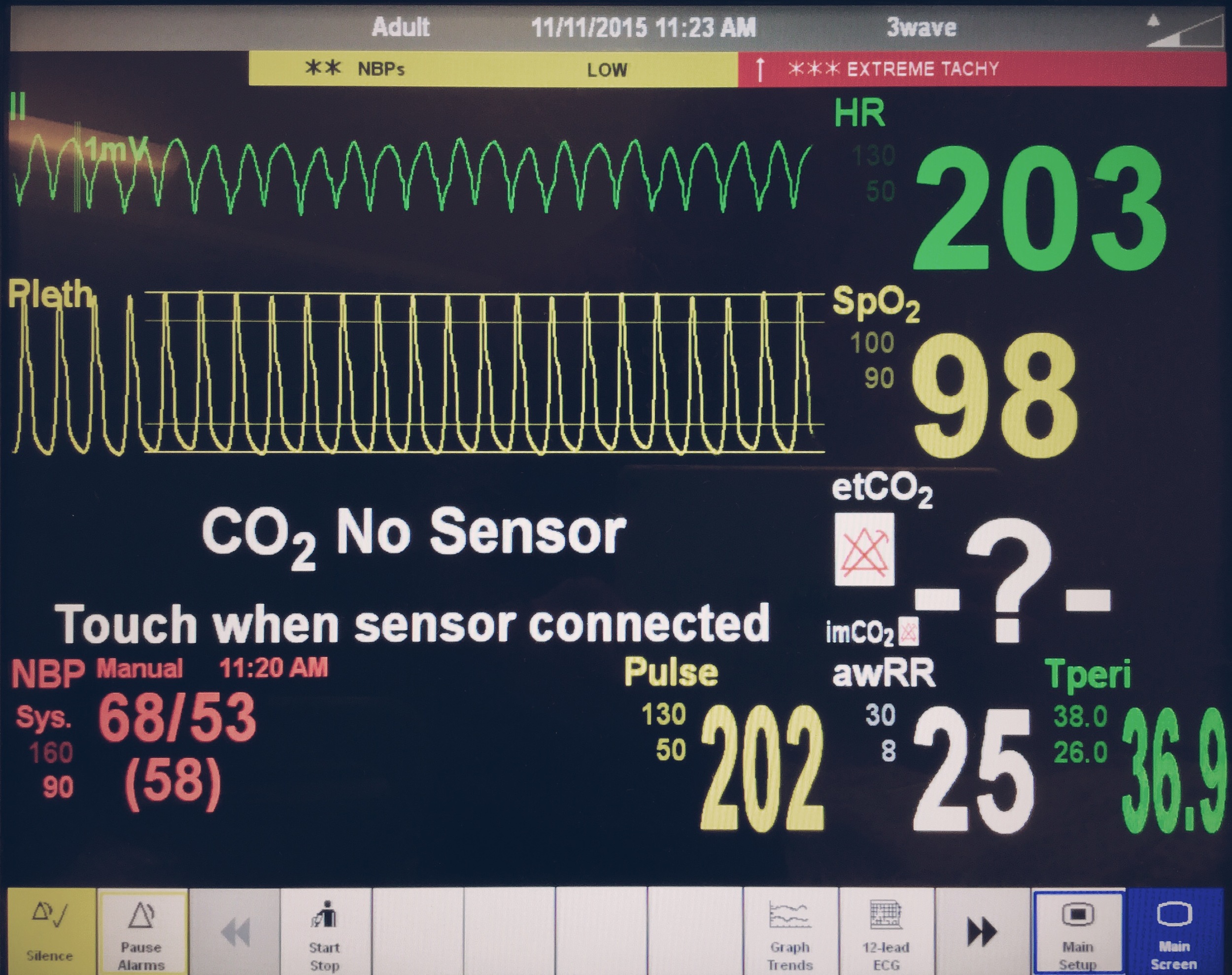
B – Sats 96%, RR 24
C – HR 121, BP 104/57
D – GCS E2 V2 M5 (9)
E – Temp 37.2°C
Clinical findings
Drowsy
Uncooperative
Why we simulated?
Tricyclic Antidepressant (TCA) overdose is a presentation that often fills clinicians with an element of fear. This is because the potential consequences of a significant ingestion can be fatal, also include arrhythmias that are difficult to treat.
From Toxbase:
"Highly toxic by ingestion.”
Ingestion of 15 mg/kg would be expected to result in serious, potentially life-threatening symptoms. Ingestion of one or two tablets by a young child may be sufficient to achieve this dose."
Suggested management:
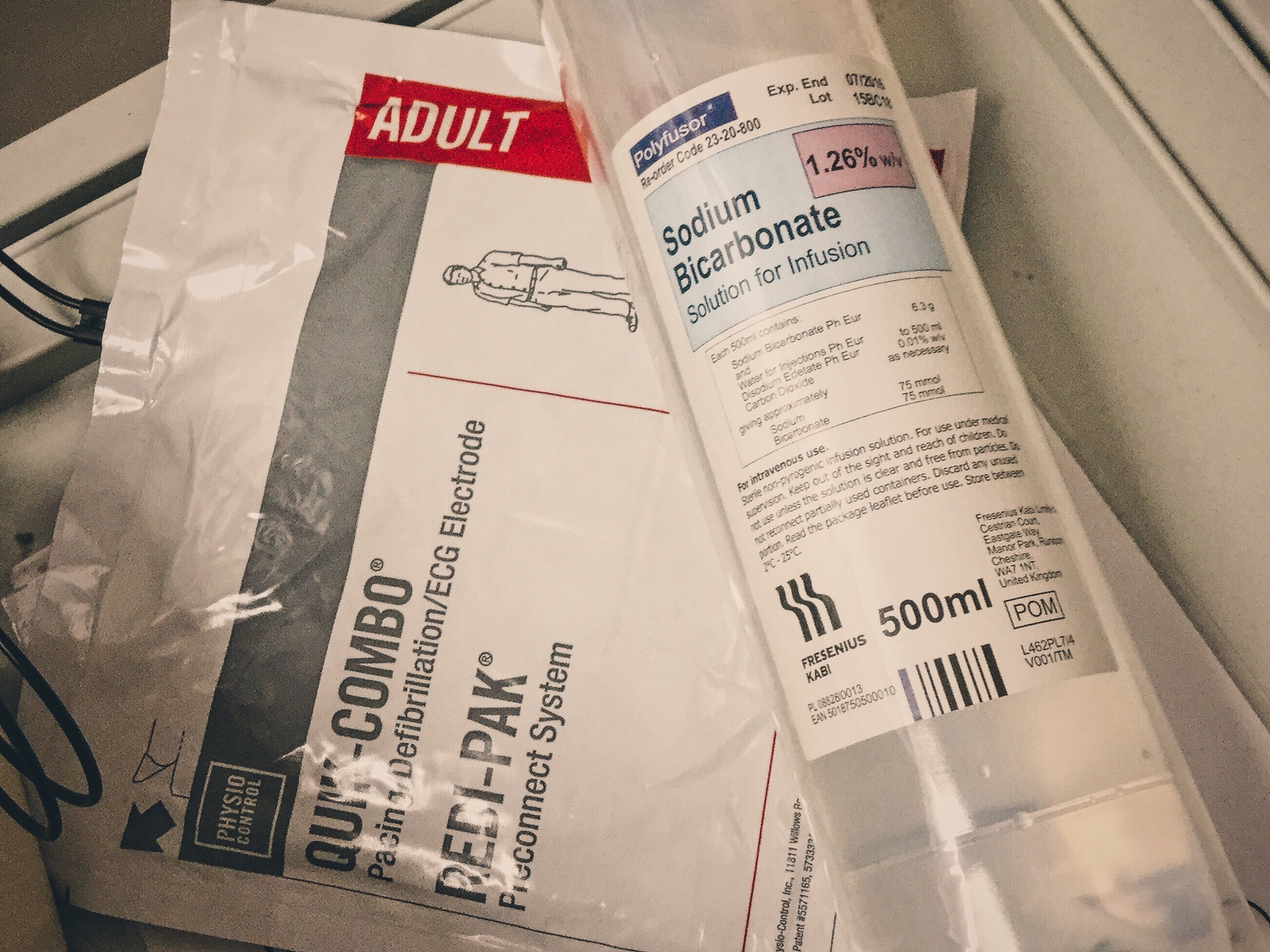
Even in the absence of an acidosis, consider alkalinisation with iv sodium bicarbonate in patients with:
QRS duration greater than 120 msec
Arrhythmias
Hypotension resistant to fluid resuscitation
There is also discussion around the use of intralipid - although use should be guided by a senior clinicians or advice of the Poisons Information Service.
| K+ Channel Blockade | QTC Prolongation |
| NE & Serotonin Reuptake Inhibition | Initial hypertension quickly followed by hypotension |
| Na+ Channel Blockade |
QRS Prolongation
Hypotension — depresses myocardial contractility Ventricular dysrhythmias Brugada-like findings on ECG |
| Muscarinic Anticholinergic Receptor Antagonism | Anticholinergic Toxidrome |
| Antihistaminergic | CNS stimulation or sedation |
| Alpha1 Adrenergic Antagonism | Hypotension |
| GABA-A Receptor Blockade | Seizures |
Further Reading:
- BMJ – Best Practice
- EMcrit – Podcast 98
Positive feedback
Recognised abnormal ECG and possibility of TCA OD
Pre-planned key Resus information (WETFLAG)
Learning outcomes
You may not know exactly what tablets a person has taken and may need to act on a "best guess".
Consider Sodium Bicarb, magnesium and intralipid for TCA overdose.
Early involvement of critical care is important.
If the team leader verbalises their thoughts it can help team members understand why actions/ drugs are needed.